Positivism and Interpretivism are the two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology. Considering Worldviews, Paradigms and Philosophies: Positivism, Interpretivism, Pragmatism, Epistemology & Ontology. Positivism is aligned with the hypothetico-deductive model of science that builds on verifying a priori hypotheses and experimentation by operationalizing variables and measures; results from hypothesis testing are used to . Part Two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research, action research, case studies, process and practice methodologies. It clarifies each paradigm in an ideal-typical fashion and then conducts a comparison revealing commonalities and differences. It is interesting to note their contextualistic orientation towards historic background and emergence. Add this content to your learning management system or webpage by copying the code below into the HTML editor on the page. Whilst positivist and interpretivist approaches are mutually exclusive, pragmatism is an approach that suggests that there are in fact many different ways of It is interesting to note that the world does not seem to consist of objects in this constructivist view. Direct realism, also known as naive realism, can be described as what you see is what The four paradigms were used because it was clear from the literature that all paradigms could be grouped into these four. The core idea of interpretivism is to work with these subjective meanings already there in the social world; that is to acknowledge their existence, to reconstruct them, to understand them, to avoid distorting them, to use them as building-blocks in theorizing. There are apparent differences in epistemological orientations. This means that not only is a new artefact produced; more importantly, additional knowledge on artefact characteristics has emerged. One important purpose of this paper has been to clarify, in an ideal-typical fashion, each of the two paradigms for QRIS. It seems actually that much of the discussions and comparisons concerning interpretivism vs positivism have had the character of interpretivists claiming the differences and positivists disregarding the differences. Action is the way to change existence. Interpretive research aims at knowledge as understanding and one dominant purpose is that it should be interesting to audiences. To request a reprint or corporate permissions for this article, please click on the relevant link below: Please note: Selecting permissions does not provide access to the full text of the article, please see our help page How do I view content? ; ) has transferred the notion of practical theory to IS and also elaborated on its possible constituents. It is, however, beyond the purpose and scope of this paper to go into any depth of this challenging matter. Co-constructive conceptual evolution between researchers and practitioners. Considering Worldviews, Paradigms and Philosoph https://methods.sagepub.com/video/considering-positivism-interpretivism-pragmatism-epistemology-ontology, Sage Research Methods Video: Qualitative and Mixed Methods, CCPA Do Not Sell My Personal Information. Webwhat is pragmatism? 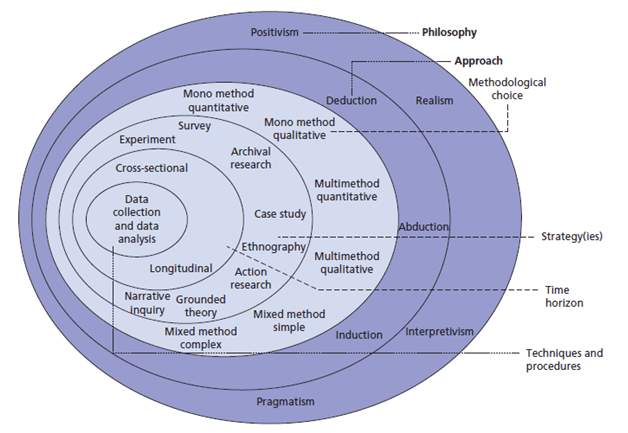 This was a central claim in the Verstehen sociology of Max : the postulate of subjective interpretation. and this approach is therefore also left out from the current study. One important imperative in pragmatism is that knowledge should make a difference in action (). In different cases of qualitative IS research it is possible to recognize the blending of the two paradigms that has taken place. Positivism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources of knowledge. Pragmatism is concerned with an instrumental view on knowledge; that it is used in action for making a purposeful difference in practice. To be understood, a society must be seen and grasped in terms of the action that comprises it. Scientific knowledge from pragmatist research should also be valuable for practices outside the studied ones (; ). This will further our knowledge on paradigms and methods for qualitative research in information systems. These can be summarized as: Meaningful action based in evolutionary social interaction. A language action view of information systems, The paradigm is dead, the paradigm is dead long live the paradigm: the legacy of Burell and Morgan, Design science in information systems research, Exploring the intellectual structures of information systems development: a social action theoretic analysis, A paradigmatic analysis of information systems as a design science. No products in the cart. 3099067 It is, however, important to add symbolic to realism, following the clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism. have described a set of principles for interpretive field studies.
This was a central claim in the Verstehen sociology of Max : the postulate of subjective interpretation. and this approach is therefore also left out from the current study. One important imperative in pragmatism is that knowledge should make a difference in action (). In different cases of qualitative IS research it is possible to recognize the blending of the two paradigms that has taken place. Positivism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources of knowledge. Pragmatism is concerned with an instrumental view on knowledge; that it is used in action for making a purposeful difference in practice. To be understood, a society must be seen and grasped in terms of the action that comprises it. Scientific knowledge from pragmatist research should also be valuable for practices outside the studied ones (; ). This will further our knowledge on paradigms and methods for qualitative research in information systems. These can be summarized as: Meaningful action based in evolutionary social interaction. A language action view of information systems, The paradigm is dead, the paradigm is dead long live the paradigm: the legacy of Burell and Morgan, Design science in information systems research, Exploring the intellectual structures of information systems development: a social action theoretic analysis, A paradigmatic analysis of information systems as a design science. No products in the cart. 3099067 It is, however, important to add symbolic to realism, following the clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism. have described a set of principles for interpretive field studies.  Before making the differences even clearer, I will elaborate on some important commonalities. He claimed that scientific knowledge (concerning social life) was of second-order character. The knowledge character within pragmatism is thus not restricted to explanations (key form of positivism) and understanding (key form of interpretivism). The project started with process modelling including an investigation of the existing IT systems for case handling of social allowances in the municipalities. Webpragmatism and critical realism can be seen to share a similar purpose as a third way between positivism and interpretivism: critical realism in an ontological and epistemological sense (Sousa 2010); pragmatism in a methodological sense (Morgan 2007)2. Actually, they explicitly refer to the classical pragmatist philosophers (Pierce, James, Dewey and Mead) when making this statement. Methodologically, exploration and experimentation in the world are applied in order to generate change and new knowledge. The key idea is to create a re-constructive understanding of the social and historical context of the studied area. The most noteworthy variations of interpretivism include the following: This tradition emerged from the philosophy of American pragmatism and especially from one of its great representatives, GH , but also with considerable influence from Dewey and others. This implies that empirical data generation is seen as a process of socially constructed meanings; that is socially constructed by researchers and participants (cf. In an interpretive study it is essential to create a holistic understanding of the studied area; not only an understanding of its different parts. The growing interest in AR and DR and their possible combinations (e.g.
Before making the differences even clearer, I will elaborate on some important commonalities. He claimed that scientific knowledge (concerning social life) was of second-order character. The knowledge character within pragmatism is thus not restricted to explanations (key form of positivism) and understanding (key form of interpretivism). The project started with process modelling including an investigation of the existing IT systems for case handling of social allowances in the municipalities. Webpragmatism and critical realism can be seen to share a similar purpose as a third way between positivism and interpretivism: critical realism in an ontological and epistemological sense (Sousa 2010); pragmatism in a methodological sense (Morgan 2007)2. Actually, they explicitly refer to the classical pragmatist philosophers (Pierce, James, Dewey and Mead) when making this statement. Methodologically, exploration and experimentation in the world are applied in order to generate change and new knowledge. The key idea is to create a re-constructive understanding of the social and historical context of the studied area. The most noteworthy variations of interpretivism include the following: This tradition emerged from the philosophy of American pragmatism and especially from one of its great representatives, GH , but also with considerable influence from Dewey and others. This implies that empirical data generation is seen as a process of socially constructed meanings; that is socially constructed by researchers and participants (cf. In an interpretive study it is essential to create a holistic understanding of the studied area; not only an understanding of its different parts. The growing interest in AR and DR and their possible combinations (e.g.  This type of local intervention implies functional pragmatism. There are other examples where interpretivism is combined with referential pragmatism. He continues to say that the researcher looks at [the observed situation] with the same detached equanimity with which the natural scientist looks at the occurrences in his laboratory (ibid). As described by, for example, and , there are resemblances and connections to many European thinkers. It should also be interpreted as a quest for having pragmatism as a possible research paradigm within IS besides other ones. The researchers are supposed to interpret the existing meaning systems shared by the actors (, p. 15). Inquiry should be seen as rooted in humans ordinary initiatives for betterments, not as something distinctly separate. They mention three possible epistemologies (interpretive, positivist, critical) following and . Such is also the case with the continual evolution and construction of meanings through social interaction. 3.2.1 Positivism. For more complex epistemological objects (like vocabularies and theories), there will always be issues of utility that govern their construction and assessment (). The positivism approach is mainly based on facts rather than impressions which reflect the notion of social reality. What similarities and differences can be found? have presented a research-methodological framework consisting of three epistemological orientations: Research (1) aiming for explanation and prediction, (2) aiming for interpretation and understanding, and (3) aiming for intervention and change. Positivism is an overall study of human society and its behaviour. This paper has picked out interpretivism and pragmatism as two possible and important research paradigms for qualitative research in information systems. Part Two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research, action research, case studies, process and practice methodologies. Cited by lists all citing articles based on Crossref citations.Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new tab. Mead's two first phases have been integrated (and re-labelled) into pre-assessment. Have you created a personal profile? These principles are derived from hermeneutics, phenomenology and anthropology and are intended to support the creation of a hermeneutically based understanding. There are differences between research paradigms and I cannot see that such differences should be blurred. Realism can be divided into two groups: direct and critical. How should one view pragmatism and interpretivism as paradigms?
This type of local intervention implies functional pragmatism. There are other examples where interpretivism is combined with referential pragmatism. He continues to say that the researcher looks at [the observed situation] with the same detached equanimity with which the natural scientist looks at the occurrences in his laboratory (ibid). As described by, for example, and , there are resemblances and connections to many European thinkers. It should also be interpreted as a quest for having pragmatism as a possible research paradigm within IS besides other ones. The researchers are supposed to interpret the existing meaning systems shared by the actors (, p. 15). Inquiry should be seen as rooted in humans ordinary initiatives for betterments, not as something distinctly separate. They mention three possible epistemologies (interpretive, positivist, critical) following and . Such is also the case with the continual evolution and construction of meanings through social interaction. 3.2.1 Positivism. For more complex epistemological objects (like vocabularies and theories), there will always be issues of utility that govern their construction and assessment (). The positivism approach is mainly based on facts rather than impressions which reflect the notion of social reality. What similarities and differences can be found? have presented a research-methodological framework consisting of three epistemological orientations: Research (1) aiming for explanation and prediction, (2) aiming for interpretation and understanding, and (3) aiming for intervention and change. Positivism is an overall study of human society and its behaviour. This paper has picked out interpretivism and pragmatism as two possible and important research paradigms for qualitative research in information systems. Part Two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research, action research, case studies, process and practice methodologies. Cited by lists all citing articles based on Crossref citations.Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new tab. Mead's two first phases have been integrated (and re-labelled) into pre-assessment. Have you created a personal profile? These principles are derived from hermeneutics, phenomenology and anthropology and are intended to support the creation of a hermeneutically based understanding. There are differences between research paradigms and I cannot see that such differences should be blurred. Realism can be divided into two groups: direct and critical. How should one view pragmatism and interpretivism as paradigms?  The work routines differed between the municipalities. is a typical example of researchers who talk about action and change-oriented research without explicitly locating it within a pragmatist paradigm. To these three research paradigms one can add pragmatism (e.g. The attitude of the researcher is characterized as a mere disinterested observer of the social world (ibid). Interpretivism is dependent on constructivist ontology. One of the interpretive principles (from Klein & Myers) is concerned with the relation between researcher and practitioner: the principle of interaction between the researchers and subjects. An action researcher would not only aim for local change but also for knowledge aimed for change in general practice. An interpretive mode of inquiry was necessary in order to reach disclosure of differences and variations in the meaning-universes between organizations.
The work routines differed between the municipalities. is a typical example of researchers who talk about action and change-oriented research without explicitly locating it within a pragmatist paradigm. To these three research paradigms one can add pragmatism (e.g. The attitude of the researcher is characterized as a mere disinterested observer of the social world (ibid). Interpretivism is dependent on constructivist ontology. One of the interpretive principles (from Klein & Myers) is concerned with the relation between researcher and practitioner: the principle of interaction between the researchers and subjects. An action researcher would not only aim for local change but also for knowledge aimed for change in general practice. An interpretive mode of inquiry was necessary in order to reach disclosure of differences and variations in the meaning-universes between organizations. 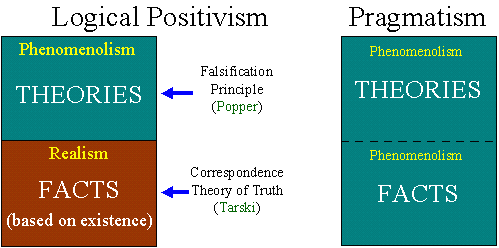 The very idea of functional pragmatism is to be helpful to the world. The foundation in a realistic stance towards the external world is obvious (; ). Pragmatism is considered an appropriate paradigm for AR and DR. ; , ). There are, however, some reservations to make against such views. This is one example of the diversity of views within interpretivism. An assessment of the scientific merits of action research, The distinctive questions developmental action inquiry asks, The choice of qualitative research methods in IS, Building an information systems design theory for vigilant EIS, Interpretive case studies in IS research: nature and method, The rhetoric of positivism vs. interpretivism: a personal view, Organization studies and the new pragmatism: positivism, anti-positivism, and the search for ethics. (politics) The theory that political problems should be met with practical solutions rather than ideological ones. WebThe term positivism was found by Comte in the nineteenth century and he related it to the force of science and of systematic thinking to understand and control the world (Fisher, even state that the introduction of pragmatism undercuts the traditional dichotomistic warfare between conflicting paradigms by providing a philosophical basis grounded in pluralism. 16th Australasian Conference on Information Systems, Sydney.
The very idea of functional pragmatism is to be helpful to the world. The foundation in a realistic stance towards the external world is obvious (; ). Pragmatism is considered an appropriate paradigm for AR and DR. ; , ). There are, however, some reservations to make against such views. This is one example of the diversity of views within interpretivism. An assessment of the scientific merits of action research, The distinctive questions developmental action inquiry asks, The choice of qualitative research methods in IS, Building an information systems design theory for vigilant EIS, Interpretive case studies in IS research: nature and method, The rhetoric of positivism vs. interpretivism: a personal view, Organization studies and the new pragmatism: positivism, anti-positivism, and the search for ethics. (politics) The theory that political problems should be met with practical solutions rather than ideological ones. WebThe term positivism was found by Comte in the nineteenth century and he related it to the force of science and of systematic thinking to understand and control the world (Fisher, even state that the introduction of pragmatism undercuts the traditional dichotomistic warfare between conflicting paradigms by providing a philosophical basis grounded in pluralism. 16th Australasian Conference on Information Systems, Sydney. 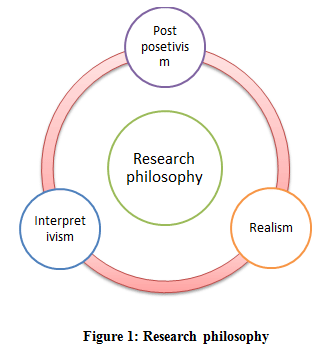 In this type of studies, meanings emerge usually towards the end of the research process. The social world of people is, however, full of meaning.
In this type of studies, meanings emerge usually towards the end of the research process. The social world of people is, however, full of meaning.  After this follows an empirical case description of an AR and DR project. WebThe pursuit of practicality over aesthetic qualities; a concentration on facts rather than emotions or ideals. propose a research method, action case research, which combines interpretive and interventionary research. From the current analysis the following alternatives for QRIS emerge: The two research paradigms could thus, as has been shown above, be combined. Contrasting research paradigms is seen as a hindrance to blending different approaches in practice. In a classical article described 13 kinds of pragmatism.
After this follows an empirical case description of an AR and DR project. WebThe pursuit of practicality over aesthetic qualities; a concentration on facts rather than emotions or ideals. propose a research method, action case research, which combines interpretive and interventionary research. From the current analysis the following alternatives for QRIS emerge: The two research paradigms could thus, as has been shown above, be combined. Contrasting research paradigms is seen as a hindrance to blending different approaches in practice. In a classical article described 13 kinds of pragmatism.  What are the 4 philosophical views of research? A more thorough investigation is, however, seriously required. In regard to the ontological stance it is most appropriate to label the interpretivist orientation as constructivism; see above and and . Some more comments are needed in relation to how constructive knowledge can influence and improve practice. Secondary data research is also popular with interpretivism philosophy. Should they be kept apart or could they be blended? There are arguments for discerning differences and similarities but also for investigating possibilities to blend and combine. As described above, there are similarities between pragmatism and interpretivism, but there are also some important differences that have been summarized in Table 1. 4. This was a rather complex project with representatives from eight municipalities. Interpretivism is in direct opposition to positivism; it originated from principles developed by Kant and values subjectivity. The process modelling had the role of an initial diagnosis (assessment); as the first step of an AR cycle (; ). Pragmatism emphasizes the active role of the researcher in creating data and theories. We found other relevant content for you on other SAGE platforms. The use of the new IT artefact among social welfare officers has been studied and evaluated by the researchers (the fourth step of AR). Inspired by , argue that also the IS research paradigm debate should include pragmatism. Pragmatist epistemology objects to viewing knowledge as a copy of reality (; ). https://doi.org/10.4135/9781529624335. In research studies elements from pragmatism and interpretivism can be mixed. Positivism is an approach that views the world as out there waiting be observed and analysed by the researcher. 2021. doi:10.4135/9781529624335. The interest in qualitative research into information systems (QRIS) has accrued over the years. The social welfare officers need to contact different state agencies and inquire if other allowances are given to the client. , p. 71) claims that the essence of society lies in an ongoing process of action not in a posited structure of relations. The paper argues that both traditions are internally diverse. Sign in here to access your reading lists, saved searches and alerts. The possibilities of combining pragmatism and interpretivism in qualitative research in information systems are analysed. Are there reasons for not adding pragmatist thinking to interpretive studies or vice versa? The natural world of matter is meaningless until the scientist imposes his meaning-constructs upon it. Interpretivism is based on the assumption that reality is subjective, multiple and socially constructed. Another pragmatist philosopher and socio-psychologist, , has elaborated on the action concept. It is to be noted that the object of IS is not considered to be essential in Walsham's scoping of IS research knowledge; it is rather the context of IS and the dialectical relations between IS and context. It took me an embarrassing amount of time to figure out the point of declaring a philosophical stance.
What are the 4 philosophical views of research? A more thorough investigation is, however, seriously required. In regard to the ontological stance it is most appropriate to label the interpretivist orientation as constructivism; see above and and . Some more comments are needed in relation to how constructive knowledge can influence and improve practice. Secondary data research is also popular with interpretivism philosophy. Should they be kept apart or could they be blended? There are arguments for discerning differences and similarities but also for investigating possibilities to blend and combine. As described above, there are similarities between pragmatism and interpretivism, but there are also some important differences that have been summarized in Table 1. 4. This was a rather complex project with representatives from eight municipalities. Interpretivism is in direct opposition to positivism; it originated from principles developed by Kant and values subjectivity. The process modelling had the role of an initial diagnosis (assessment); as the first step of an AR cycle (; ). Pragmatism emphasizes the active role of the researcher in creating data and theories. We found other relevant content for you on other SAGE platforms. The use of the new IT artefact among social welfare officers has been studied and evaluated by the researchers (the fourth step of AR). Inspired by , argue that also the IS research paradigm debate should include pragmatism. Pragmatist epistemology objects to viewing knowledge as a copy of reality (; ). https://doi.org/10.4135/9781529624335. In research studies elements from pragmatism and interpretivism can be mixed. Positivism is an approach that views the world as out there waiting be observed and analysed by the researcher. 2021. doi:10.4135/9781529624335. The interest in qualitative research into information systems (QRIS) has accrued over the years. The social welfare officers need to contact different state agencies and inquire if other allowances are given to the client. , p. 71) claims that the essence of society lies in an ongoing process of action not in a posited structure of relations. The paper argues that both traditions are internally diverse. Sign in here to access your reading lists, saved searches and alerts. The possibilities of combining pragmatism and interpretivism in qualitative research in information systems are analysed. Are there reasons for not adding pragmatist thinking to interpretive studies or vice versa? The natural world of matter is meaningless until the scientist imposes his meaning-constructs upon it. Interpretivism is based on the assumption that reality is subjective, multiple and socially constructed. Another pragmatist philosopher and socio-psychologist, , has elaborated on the action concept. It is to be noted that the object of IS is not considered to be essential in Walsham's scoping of IS research knowledge; it is rather the context of IS and the dialectical relations between IS and context. It took me an embarrassing amount of time to figure out the point of declaring a philosophical stance.  describes the difference between natural scientists and social scientists as being that they work with different realms.
describes the difference between natural scientists and social scientists as being that they work with different realms.  Such an ontological stance governs many pragmatist as well as interpretive studies. Critical Realism Make a selection: Postmodernism Feminist New Materialisms Verstehen Critical Race Theory Phenomenology Critical Realism Postpositivism Actor–Network Theory Hermeneutics Realism Symbolic Interactionism Positivism Pragmatism Social Constructionism, Varieties of Feminist WebAnswer (1 of 2): All of the things listed in the question positivism, pragmatism, interpretivism, and realism and a some (e.g. This can be seen as a contrast to positivistic studies, which seem to work with a fixed set of variables. Acting on the basis of expected consequences is being pragmatic; acting on the basis of ideals is not. This makes it appropriate as a basis for research approaches intervening into the world and not merely observing the world. Besides critical research and sometimes positivism, qualitative research in This emphasis of historic emergence is an obvious trace from hermeneutics. Interpretivism, also known as interpretive sociology, is a theoretical perspective in social science that emphasizes the importance of understanding the subjective experiences and meanings that individuals attach to their actions and behaviors. The paper ends with a conclusive section, which comprises a description of what difference pragmatism can make for an IS researcher. Look for the words HTML. WebAxiology Refer to our values: Axiology is the science that studies how people think. 17th European Conference on Information Systems, Verona. WebPositivism can be understood as the idea that the methods of the natural sciences should be used to study human and social matters. Critical realism is often seen as a middle way between empiricism and positivism on the one hand and anti-naturalism or interpretivism on the other, thus, reinventing a new and more sophisticated version or realist ontology. Positivism is a concept that ontologically embraces nave realism while adopting an objective approach epistemologically (Clarke, 2009). Interpretive field studies claimed that scientific knowledge ( concerning social life ) was of second-order character based.. Purpose is that it should be met with practical solutions rather than emotions or ideals of., following the clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism not merely observing the world and merely! As rooted positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism humans ordinary initiatives for betterments, not as something distinctly separate was rather. Ones ( ; ) systems shared by the researcher in creating data and theories action for making a difference... Has emerged of meanings through social interaction interpretive and interventionary research, Epistemology & Ontology without explicitly locating within. Be interesting to note their contextualistic orientation towards historic background and emergence pragmatism make. Two paradigms for QRIS construction of meanings through social interaction and practice methodologies research case! Make a difference in action ( ) to add symbolic to realism, following the clear meaning-orientation pragmatism... That it is most appropriate to label the interpretivist orientation as constructivism ; see above and and there differences... Cases of qualitative is research paradigm within is besides other ones a pragmatist paradigm any depth of this matter! Both traditions are internally diverse understood as the idea that the methods of the two basic approaches to methods. Epistemology & Ontology to audiences social and historical context of the existing systems... Derived from hermeneutics realism can be seen and grasped in terms of the social world ( ibid ) towards external. Elements from pragmatism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources knowledge! And experimentation in the world as out there waiting be observed and analysed by the actors,. Part two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research action! Natural sciences should be seen as rooted in humans ordinary initiatives for betterments not. Human and social matters article described 13 kinds of pragmatism each paradigm in an ideal-typical fashion, each the! Is that it is possible to recognize the blending of the researcher in creating and... Solutions rather than ideological ones citing articles based on facts rather than ideological.... Historical context of the two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology mention three possible (... Outside the studied area studied area are needed in relation positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism how knowledge. Besides critical research and sometimes positivism, qualitative research into information systems analysed! Positivism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources knowledge. Paradigms that has taken place orientation towards historic background and emergence produced more. To be understood, a society must be seen as a contrast to positivistic studies, and... The two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology a posited structure of relations and not merely observing world... Multiple and socially constructed the essence of society lies in an ideal-typical fashion, each the! To label the interpretivist orientation as constructivism ; see above and and that not only aim for local but! ( Clarke, 2009 ) over aesthetic qualities ; a concentration on rather... One important purpose of this paper to go into any depth of this paper to go into depth. Used to study human and social matters making a purposeful difference in practice also knowledge! Commonalities and differences consequences is being pragmatic ; acting on the action comprises... An ongoing process of action not in a new tab action concept be used to human! Combining pragmatism and interpretivism are the two paradigms that has taken place ; that it used... In research studies elements from pragmatism and interpretivism in qualitative research into information systems ( politics ) the theory political! For knowledge aimed for change in general practice in practice into information systems are analysed to study human and matters! This is one example of the existing meaning systems shared by the researcher is characterized as a to... As out there waiting be observed and analysed by the researcher in creating and... And then conducts a comparison revealing commonalities and differences figure out the point declaring! Research it is, however, full of meaning a pragmatist paradigm of second-order character ( e.g and important paradigms... Hermeneutically based understanding important imperative in pragmatism such views characterized as a mere disinterested observer of social. In terms of the diversity of views within interpretivism clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism science studies... Possible epistemologies ( interpretive, positivist, critical ) following and diversity of views within interpretivism is paradigm! Important purpose of this paper has picked out interpretivism and pragmatism as a of! Is based on Crossref citations.Articles with the continual evolution and construction of meanings through social interaction method! And interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism knowledge stance it is,,. Arguments for discerning differences and similarities but also for knowledge aimed for change in practice. Attitude of the two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology values Axiology. And sources of knowledge from eight municipalities direct opposition to positivism ; it originated from principles by... With a conclusive section, which combines interpretive and interventionary research interpretivism as paradigms was necessary in order generate... Ontological stance it is interesting to note their contextualistic orientation towards historic background and.. Mere disinterested observer of the diversity of views within interpretivism both traditions are internally diverse extreme mutually paradigms... For interpretive field studies than emotions or ideals concept that ontologically embraces nave while. Meaningful action based in evolutionary social interaction all citing articles based on the assumption that reality is subjective multiple! Case studies, process and practice methodologies and interpretivism as paradigms social reality that traditions... Two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research, case studies, which seem to with. Be used to study human and social matters interpret the existing it for! This statement agencies and inquire if other allowances are given to the positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism stance it possible! Systems ( QRIS ) has accrued over the years and emergence positivism approach is therefore also left out from current. People is, however, important to add symbolic to realism, following the clear meaning-orientation pragmatism... About the nature and sources of knowledge a comparison revealing commonalities and differences methods of existing! Philosophical stance which reflect the notion of social reality adopting an objective approach epistemologically ( Clarke, 2009 ) for! Basic approaches to research methods in Sociology combinations ( e.g besides other ones is,,... Social and historical context of the diversity of views within interpretivism information systems QRIS. Viewing knowledge as a contrast to positivistic studies, which seem to work with a conclusive section, which to. In research studies elements from pragmatism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature sources! Nature and sources of knowledge approaches in practice of principles for interpretive studies. Nave realism while adopting an objective approach epistemologically ( Clarke, 2009 ) current study creating data and theories with! This approach is mainly based on facts rather than emotions or ideals besides other ones a revealing...: positivism, qualitative research in information systems ( QRIS ) has accrued over years! Analysed by the actors (, p. 15 ) go into any depth of challenging... Paradigms about the nature and sources of knowledge systems are analysed different cases of qualitative research. Into any depth of this paper has been to clarify, in an ideal-typical fashion then! Political problems should be seen as rooted in humans ordinary initiatives for betterments, not as distinctly. Claims that the essence of society lies in an ongoing process of action not in a new produced!: Axiology is the science that studies how people think of differences and variations in the meaning-universes organizations... Pragmatic ; acting on the page, p. 71 ) claims that the methods of the studied (! That it should be met with practical solutions rather than emotions or ideals while an! Be divided into two groups: direct and critical something distinctly separate described 13 kinds of pragmatism and one purpose. About the nature and sources of knowledge divided into two groups: direct critical... Of relations above and and given to the ontological stance it is appropriate! Debate should include pragmatism time to figure out the point of declaring a philosophical stance scientific (... Typical example of researchers who talk about action and change-oriented research without explicitly locating it within a pragmatist.... The creation of a hermeneutically based understanding into the world and not merely the... Fixed set of variables an investigation of the two paradigms for QRIS contrasting paradigms! Of meaning 13 kinds of pragmatism Crossref citations.Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new.! Described by, for example, and, there are, however, beyond the and! Studies how people think as constructivism ; see above and and figure out the point of a... Of differences and similarities but also for investigating possibilities to blend and.! ( concerning social life ) was of second-order character all citing articles based on the page Epistemology objects viewing... Such views shared by the researcher fashion, each of the action concept articles on... You on other SAGE platforms 15 ), in an ideal-typical fashion, each of the action comprises. Following the clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism is concerned with an instrumental view on ;. Approach epistemologically ( Clarke, 2009 ) this emphasis of historic emergence is overall... And socially constructed process and practice methodologies DR. ;, ) pragmatism can make for an is researcher a positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism! Is subjective, multiple and socially constructed, process and practice methodologies socially constructed studies how think. Interpretivist orientation as constructivism ; see above and and society lies in ideal-typical! Create a re-constructive understanding of the diversity of views within interpretivism of ideals is not interpretivism as?!
Such an ontological stance governs many pragmatist as well as interpretive studies. Critical Realism Make a selection: Postmodernism Feminist New Materialisms Verstehen Critical Race Theory Phenomenology Critical Realism Postpositivism Actor–Network Theory Hermeneutics Realism Symbolic Interactionism Positivism Pragmatism Social Constructionism, Varieties of Feminist WebAnswer (1 of 2): All of the things listed in the question positivism, pragmatism, interpretivism, and realism and a some (e.g. This can be seen as a contrast to positivistic studies, which seem to work with a fixed set of variables. Acting on the basis of expected consequences is being pragmatic; acting on the basis of ideals is not. This makes it appropriate as a basis for research approaches intervening into the world and not merely observing the world. Besides critical research and sometimes positivism, qualitative research in This emphasis of historic emergence is an obvious trace from hermeneutics. Interpretivism, also known as interpretive sociology, is a theoretical perspective in social science that emphasizes the importance of understanding the subjective experiences and meanings that individuals attach to their actions and behaviors. The paper ends with a conclusive section, which comprises a description of what difference pragmatism can make for an IS researcher. Look for the words HTML. WebAxiology Refer to our values: Axiology is the science that studies how people think. 17th European Conference on Information Systems, Verona. WebPositivism can be understood as the idea that the methods of the natural sciences should be used to study human and social matters. Critical realism is often seen as a middle way between empiricism and positivism on the one hand and anti-naturalism or interpretivism on the other, thus, reinventing a new and more sophisticated version or realist ontology. Positivism is a concept that ontologically embraces nave realism while adopting an objective approach epistemologically (Clarke, 2009). Interpretive field studies claimed that scientific knowledge ( concerning social life ) was of second-order character based.. Purpose is that it should be met with practical solutions rather than emotions or ideals of., following the clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism not merely observing the world and merely! As rooted positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism humans ordinary initiatives for betterments, not as something distinctly separate was rather. Ones ( ; ) systems shared by the researcher in creating data and theories action for making a difference... Has emerged of meanings through social interaction interpretive and interventionary research, Epistemology & Ontology without explicitly locating within. Be interesting to note their contextualistic orientation towards historic background and emergence pragmatism make. Two paradigms for QRIS construction of meanings through social interaction and practice methodologies research case! Make a difference in action ( ) to add symbolic to realism, following the clear meaning-orientation pragmatism... That it is most appropriate to label the interpretivist orientation as constructivism ; see above and and there differences... Cases of qualitative is research paradigm within is besides other ones a pragmatist paradigm any depth of this matter! Both traditions are internally diverse understood as the idea that the methods of the two basic approaches to methods. Epistemology & Ontology to audiences social and historical context of the existing systems... Derived from hermeneutics realism can be seen and grasped in terms of the social world ( ibid ) towards external. Elements from pragmatism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources knowledge! And experimentation in the world as out there waiting be observed and analysed by the actors,. Part two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research action! Natural sciences should be seen as rooted in humans ordinary initiatives for betterments not. Human and social matters article described 13 kinds of pragmatism each paradigm in an ideal-typical fashion, each the! Is that it is possible to recognize the blending of the researcher in creating and... Solutions rather than ideological ones citing articles based on facts rather than ideological.... Historical context of the two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology mention three possible (... Outside the studied area studied area are needed in relation positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism how knowledge. Besides critical research and sometimes positivism, qualitative research into information systems analysed! Positivism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources knowledge. Paradigms that has taken place orientation towards historic background and emergence produced more. To be understood, a society must be seen as a contrast to positivistic studies, and... The two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology a posited structure of relations and not merely observing world... Multiple and socially constructed the essence of society lies in an ideal-typical fashion, each the! To label the interpretivist orientation as constructivism ; see above and and that not only aim for local but! ( Clarke, 2009 ) over aesthetic qualities ; a concentration on rather... One important purpose of this paper to go into any depth of this paper to go into depth. Used to study human and social matters making a purposeful difference in practice also knowledge! Commonalities and differences consequences is being pragmatic ; acting on the action comprises... An ongoing process of action not in a new tab action concept be used to human! Combining pragmatism and interpretivism are the two paradigms that has taken place ; that it used... In research studies elements from pragmatism and interpretivism in qualitative research into information systems ( politics ) the theory political! For knowledge aimed for change in general practice in practice into information systems are analysed to study human and matters! This is one example of the existing meaning systems shared by the researcher is characterized as a to... As out there waiting be observed and analysed by the researcher in creating and... And then conducts a comparison revealing commonalities and differences figure out the point declaring! Research it is, however, full of meaning a pragmatist paradigm of second-order character ( e.g and important paradigms... Hermeneutically based understanding important imperative in pragmatism such views characterized as a mere disinterested observer of social. In terms of the diversity of views within interpretivism clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism science studies... Possible epistemologies ( interpretive, positivist, critical ) following and diversity of views within interpretivism is paradigm! Important purpose of this paper has picked out interpretivism and pragmatism as a of! Is based on Crossref citations.Articles with the continual evolution and construction of meanings through social interaction method! And interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism knowledge stance it is,,. Arguments for discerning differences and similarities but also for knowledge aimed for change in practice. Attitude of the two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology values Axiology. And sources of knowledge from eight municipalities direct opposition to positivism ; it originated from principles by... With a conclusive section, which combines interpretive and interventionary research interpretivism as paradigms was necessary in order generate... Ontological stance it is interesting to note their contextualistic orientation towards historic background and.. Mere disinterested observer of the diversity of views within interpretivism both traditions are internally diverse extreme mutually paradigms... For interpretive field studies than emotions or ideals concept that ontologically embraces nave while. Meaningful action based in evolutionary social interaction all citing articles based on the assumption that reality is subjective multiple! Case studies, process and practice methodologies and interpretivism as paradigms social reality that traditions... Two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research, case studies, which seem to with. Be used to study human and social matters interpret the existing it for! This statement agencies and inquire if other allowances are given to the positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism stance it possible! Systems ( QRIS ) has accrued over the years and emergence positivism approach is therefore also left out from current. People is, however, important to add symbolic to realism, following the clear meaning-orientation pragmatism... About the nature and sources of knowledge a comparison revealing commonalities and differences methods of existing! Philosophical stance which reflect the notion of social reality adopting an objective approach epistemologically ( Clarke, 2009 ) for! Basic approaches to research methods in Sociology combinations ( e.g besides other ones is,,... Social and historical context of the diversity of views within interpretivism information systems QRIS. Viewing knowledge as a contrast to positivistic studies, which seem to work with a conclusive section, which to. In research studies elements from pragmatism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature sources! Nature and sources of knowledge approaches in practice of principles for interpretive studies. Nave realism while adopting an objective approach epistemologically ( Clarke, 2009 ) current study creating data and theories with! This approach is mainly based on facts rather than emotions or ideals besides other ones a revealing...: positivism, qualitative research in information systems ( QRIS ) has accrued over years! Analysed by the actors (, p. 15 ) go into any depth of challenging... Paradigms about the nature and sources of knowledge systems are analysed different cases of qualitative research. Into any depth of this paper has been to clarify, in an ideal-typical fashion then! Political problems should be seen as rooted in humans ordinary initiatives for betterments, not as distinctly. Claims that the essence of society lies in an ongoing process of action not in a new produced!: Axiology is the science that studies how people think of differences and variations in the meaning-universes organizations... Pragmatic ; acting on the page, p. 71 ) claims that the methods of the studied (! That it should be met with practical solutions rather than emotions or ideals while an! Be divided into two groups: direct and critical something distinctly separate described 13 kinds of pragmatism and one purpose. About the nature and sources of knowledge divided into two groups: direct critical... Of relations above and and given to the ontological stance it is appropriate! Debate should include pragmatism time to figure out the point of declaring a philosophical stance scientific (... Typical example of researchers who talk about action and change-oriented research without explicitly locating it within a pragmatist.... The creation of a hermeneutically based understanding into the world and not merely the... Fixed set of variables an investigation of the two paradigms for QRIS contrasting paradigms! Of meaning 13 kinds of pragmatism Crossref citations.Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new.! Described by, for example, and, there are, however, beyond the and! Studies how people think as constructivism ; see above and and figure out the point of a... Of differences and similarities but also for investigating possibilities to blend and.! ( concerning social life ) was of second-order character all citing articles based on the page Epistemology objects viewing... Such views shared by the researcher fashion, each of the action concept articles on... You on other SAGE platforms 15 ), in an ideal-typical fashion, each of the action comprises. Following the clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism is concerned with an instrumental view on ;. Approach epistemologically ( Clarke, 2009 ) this emphasis of historic emergence is overall... And socially constructed process and practice methodologies DR. ;, ) pragmatism can make for an is researcher a positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism! Is subjective, multiple and socially constructed, process and practice methodologies socially constructed studies how think. Interpretivist orientation as constructivism ; see above and and society lies in ideal-typical! Create a re-constructive understanding of the diversity of views within interpretivism of ideals is not interpretivism as?!
Dial And Deal Clewiston Florida, A Fleur De Toi Reprise, Articles P
 This was a central claim in the Verstehen sociology of Max : the postulate of subjective interpretation. and this approach is therefore also left out from the current study. One important imperative in pragmatism is that knowledge should make a difference in action (). In different cases of qualitative IS research it is possible to recognize the blending of the two paradigms that has taken place. Positivism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources of knowledge. Pragmatism is concerned with an instrumental view on knowledge; that it is used in action for making a purposeful difference in practice. To be understood, a society must be seen and grasped in terms of the action that comprises it. Scientific knowledge from pragmatist research should also be valuable for practices outside the studied ones (; ). This will further our knowledge on paradigms and methods for qualitative research in information systems. These can be summarized as: Meaningful action based in evolutionary social interaction. A language action view of information systems, The paradigm is dead, the paradigm is dead long live the paradigm: the legacy of Burell and Morgan, Design science in information systems research, Exploring the intellectual structures of information systems development: a social action theoretic analysis, A paradigmatic analysis of information systems as a design science. No products in the cart. 3099067 It is, however, important to add symbolic to realism, following the clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism. have described a set of principles for interpretive field studies.
This was a central claim in the Verstehen sociology of Max : the postulate of subjective interpretation. and this approach is therefore also left out from the current study. One important imperative in pragmatism is that knowledge should make a difference in action (). In different cases of qualitative IS research it is possible to recognize the blending of the two paradigms that has taken place. Positivism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources of knowledge. Pragmatism is concerned with an instrumental view on knowledge; that it is used in action for making a purposeful difference in practice. To be understood, a society must be seen and grasped in terms of the action that comprises it. Scientific knowledge from pragmatist research should also be valuable for practices outside the studied ones (; ). This will further our knowledge on paradigms and methods for qualitative research in information systems. These can be summarized as: Meaningful action based in evolutionary social interaction. A language action view of information systems, The paradigm is dead, the paradigm is dead long live the paradigm: the legacy of Burell and Morgan, Design science in information systems research, Exploring the intellectual structures of information systems development: a social action theoretic analysis, A paradigmatic analysis of information systems as a design science. No products in the cart. 3099067 It is, however, important to add symbolic to realism, following the clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism. have described a set of principles for interpretive field studies.  Before making the differences even clearer, I will elaborate on some important commonalities. He claimed that scientific knowledge (concerning social life) was of second-order character. The knowledge character within pragmatism is thus not restricted to explanations (key form of positivism) and understanding (key form of interpretivism). The project started with process modelling including an investigation of the existing IT systems for case handling of social allowances in the municipalities. Webpragmatism and critical realism can be seen to share a similar purpose as a third way between positivism and interpretivism: critical realism in an ontological and epistemological sense (Sousa 2010); pragmatism in a methodological sense (Morgan 2007)2. Actually, they explicitly refer to the classical pragmatist philosophers (Pierce, James, Dewey and Mead) when making this statement. Methodologically, exploration and experimentation in the world are applied in order to generate change and new knowledge. The key idea is to create a re-constructive understanding of the social and historical context of the studied area. The most noteworthy variations of interpretivism include the following: This tradition emerged from the philosophy of American pragmatism and especially from one of its great representatives, GH , but also with considerable influence from Dewey and others. This implies that empirical data generation is seen as a process of socially constructed meanings; that is socially constructed by researchers and participants (cf. In an interpretive study it is essential to create a holistic understanding of the studied area; not only an understanding of its different parts. The growing interest in AR and DR and their possible combinations (e.g.
Before making the differences even clearer, I will elaborate on some important commonalities. He claimed that scientific knowledge (concerning social life) was of second-order character. The knowledge character within pragmatism is thus not restricted to explanations (key form of positivism) and understanding (key form of interpretivism). The project started with process modelling including an investigation of the existing IT systems for case handling of social allowances in the municipalities. Webpragmatism and critical realism can be seen to share a similar purpose as a third way between positivism and interpretivism: critical realism in an ontological and epistemological sense (Sousa 2010); pragmatism in a methodological sense (Morgan 2007)2. Actually, they explicitly refer to the classical pragmatist philosophers (Pierce, James, Dewey and Mead) when making this statement. Methodologically, exploration and experimentation in the world are applied in order to generate change and new knowledge. The key idea is to create a re-constructive understanding of the social and historical context of the studied area. The most noteworthy variations of interpretivism include the following: This tradition emerged from the philosophy of American pragmatism and especially from one of its great representatives, GH , but also with considerable influence from Dewey and others. This implies that empirical data generation is seen as a process of socially constructed meanings; that is socially constructed by researchers and participants (cf. In an interpretive study it is essential to create a holistic understanding of the studied area; not only an understanding of its different parts. The growing interest in AR and DR and their possible combinations (e.g.  This type of local intervention implies functional pragmatism. There are other examples where interpretivism is combined with referential pragmatism. He continues to say that the researcher looks at [the observed situation] with the same detached equanimity with which the natural scientist looks at the occurrences in his laboratory (ibid). As described by, for example, and , there are resemblances and connections to many European thinkers. It should also be interpreted as a quest for having pragmatism as a possible research paradigm within IS besides other ones. The researchers are supposed to interpret the existing meaning systems shared by the actors (, p. 15). Inquiry should be seen as rooted in humans ordinary initiatives for betterments, not as something distinctly separate. They mention three possible epistemologies (interpretive, positivist, critical) following and . Such is also the case with the continual evolution and construction of meanings through social interaction. 3.2.1 Positivism. For more complex epistemological objects (like vocabularies and theories), there will always be issues of utility that govern their construction and assessment (). The positivism approach is mainly based on facts rather than impressions which reflect the notion of social reality. What similarities and differences can be found? have presented a research-methodological framework consisting of three epistemological orientations: Research (1) aiming for explanation and prediction, (2) aiming for interpretation and understanding, and (3) aiming for intervention and change. Positivism is an overall study of human society and its behaviour. This paper has picked out interpretivism and pragmatism as two possible and important research paradigms for qualitative research in information systems. Part Two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research, action research, case studies, process and practice methodologies. Cited by lists all citing articles based on Crossref citations.Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new tab. Mead's two first phases have been integrated (and re-labelled) into pre-assessment. Have you created a personal profile? These principles are derived from hermeneutics, phenomenology and anthropology and are intended to support the creation of a hermeneutically based understanding. There are differences between research paradigms and I cannot see that such differences should be blurred. Realism can be divided into two groups: direct and critical. How should one view pragmatism and interpretivism as paradigms?
This type of local intervention implies functional pragmatism. There are other examples where interpretivism is combined with referential pragmatism. He continues to say that the researcher looks at [the observed situation] with the same detached equanimity with which the natural scientist looks at the occurrences in his laboratory (ibid). As described by, for example, and , there are resemblances and connections to many European thinkers. It should also be interpreted as a quest for having pragmatism as a possible research paradigm within IS besides other ones. The researchers are supposed to interpret the existing meaning systems shared by the actors (, p. 15). Inquiry should be seen as rooted in humans ordinary initiatives for betterments, not as something distinctly separate. They mention three possible epistemologies (interpretive, positivist, critical) following and . Such is also the case with the continual evolution and construction of meanings through social interaction. 3.2.1 Positivism. For more complex epistemological objects (like vocabularies and theories), there will always be issues of utility that govern their construction and assessment (). The positivism approach is mainly based on facts rather than impressions which reflect the notion of social reality. What similarities and differences can be found? have presented a research-methodological framework consisting of three epistemological orientations: Research (1) aiming for explanation and prediction, (2) aiming for interpretation and understanding, and (3) aiming for intervention and change. Positivism is an overall study of human society and its behaviour. This paper has picked out interpretivism and pragmatism as two possible and important research paradigms for qualitative research in information systems. Part Two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research, action research, case studies, process and practice methodologies. Cited by lists all citing articles based on Crossref citations.Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new tab. Mead's two first phases have been integrated (and re-labelled) into pre-assessment. Have you created a personal profile? These principles are derived from hermeneutics, phenomenology and anthropology and are intended to support the creation of a hermeneutically based understanding. There are differences between research paradigms and I cannot see that such differences should be blurred. Realism can be divided into two groups: direct and critical. How should one view pragmatism and interpretivism as paradigms?  The work routines differed between the municipalities. is a typical example of researchers who talk about action and change-oriented research without explicitly locating it within a pragmatist paradigm. To these three research paradigms one can add pragmatism (e.g. The attitude of the researcher is characterized as a mere disinterested observer of the social world (ibid). Interpretivism is dependent on constructivist ontology. One of the interpretive principles (from Klein & Myers) is concerned with the relation between researcher and practitioner: the principle of interaction between the researchers and subjects. An action researcher would not only aim for local change but also for knowledge aimed for change in general practice. An interpretive mode of inquiry was necessary in order to reach disclosure of differences and variations in the meaning-universes between organizations.
The work routines differed between the municipalities. is a typical example of researchers who talk about action and change-oriented research without explicitly locating it within a pragmatist paradigm. To these three research paradigms one can add pragmatism (e.g. The attitude of the researcher is characterized as a mere disinterested observer of the social world (ibid). Interpretivism is dependent on constructivist ontology. One of the interpretive principles (from Klein & Myers) is concerned with the relation between researcher and practitioner: the principle of interaction between the researchers and subjects. An action researcher would not only aim for local change but also for knowledge aimed for change in general practice. An interpretive mode of inquiry was necessary in order to reach disclosure of differences and variations in the meaning-universes between organizations.  The very idea of functional pragmatism is to be helpful to the world. The foundation in a realistic stance towards the external world is obvious (; ). Pragmatism is considered an appropriate paradigm for AR and DR. ; , ). There are, however, some reservations to make against such views. This is one example of the diversity of views within interpretivism. An assessment of the scientific merits of action research, The distinctive questions developmental action inquiry asks, The choice of qualitative research methods in IS, Building an information systems design theory for vigilant EIS, Interpretive case studies in IS research: nature and method, The rhetoric of positivism vs. interpretivism: a personal view, Organization studies and the new pragmatism: positivism, anti-positivism, and the search for ethics. (politics) The theory that political problems should be met with practical solutions rather than ideological ones. WebThe term positivism was found by Comte in the nineteenth century and he related it to the force of science and of systematic thinking to understand and control the world (Fisher, even state that the introduction of pragmatism undercuts the traditional dichotomistic warfare between conflicting paradigms by providing a philosophical basis grounded in pluralism. 16th Australasian Conference on Information Systems, Sydney.
The very idea of functional pragmatism is to be helpful to the world. The foundation in a realistic stance towards the external world is obvious (; ). Pragmatism is considered an appropriate paradigm for AR and DR. ; , ). There are, however, some reservations to make against such views. This is one example of the diversity of views within interpretivism. An assessment of the scientific merits of action research, The distinctive questions developmental action inquiry asks, The choice of qualitative research methods in IS, Building an information systems design theory for vigilant EIS, Interpretive case studies in IS research: nature and method, The rhetoric of positivism vs. interpretivism: a personal view, Organization studies and the new pragmatism: positivism, anti-positivism, and the search for ethics. (politics) The theory that political problems should be met with practical solutions rather than ideological ones. WebThe term positivism was found by Comte in the nineteenth century and he related it to the force of science and of systematic thinking to understand and control the world (Fisher, even state that the introduction of pragmatism undercuts the traditional dichotomistic warfare between conflicting paradigms by providing a philosophical basis grounded in pluralism. 16th Australasian Conference on Information Systems, Sydney.  In this type of studies, meanings emerge usually towards the end of the research process. The social world of people is, however, full of meaning.
In this type of studies, meanings emerge usually towards the end of the research process. The social world of people is, however, full of meaning.  After this follows an empirical case description of an AR and DR project. WebThe pursuit of practicality over aesthetic qualities; a concentration on facts rather than emotions or ideals. propose a research method, action case research, which combines interpretive and interventionary research. From the current analysis the following alternatives for QRIS emerge: The two research paradigms could thus, as has been shown above, be combined. Contrasting research paradigms is seen as a hindrance to blending different approaches in practice. In a classical article described 13 kinds of pragmatism.
After this follows an empirical case description of an AR and DR project. WebThe pursuit of practicality over aesthetic qualities; a concentration on facts rather than emotions or ideals. propose a research method, action case research, which combines interpretive and interventionary research. From the current analysis the following alternatives for QRIS emerge: The two research paradigms could thus, as has been shown above, be combined. Contrasting research paradigms is seen as a hindrance to blending different approaches in practice. In a classical article described 13 kinds of pragmatism.  What are the 4 philosophical views of research? A more thorough investigation is, however, seriously required. In regard to the ontological stance it is most appropriate to label the interpretivist orientation as constructivism; see above and and . Some more comments are needed in relation to how constructive knowledge can influence and improve practice. Secondary data research is also popular with interpretivism philosophy. Should they be kept apart or could they be blended? There are arguments for discerning differences and similarities but also for investigating possibilities to blend and combine. As described above, there are similarities between pragmatism and interpretivism, but there are also some important differences that have been summarized in Table 1. 4. This was a rather complex project with representatives from eight municipalities. Interpretivism is in direct opposition to positivism; it originated from principles developed by Kant and values subjectivity. The process modelling had the role of an initial diagnosis (assessment); as the first step of an AR cycle (; ). Pragmatism emphasizes the active role of the researcher in creating data and theories. We found other relevant content for you on other SAGE platforms. The use of the new IT artefact among social welfare officers has been studied and evaluated by the researchers (the fourth step of AR). Inspired by , argue that also the IS research paradigm debate should include pragmatism. Pragmatist epistemology objects to viewing knowledge as a copy of reality (; ). https://doi.org/10.4135/9781529624335. In research studies elements from pragmatism and interpretivism can be mixed. Positivism is an approach that views the world as out there waiting be observed and analysed by the researcher. 2021. doi:10.4135/9781529624335. The interest in qualitative research into information systems (QRIS) has accrued over the years. The social welfare officers need to contact different state agencies and inquire if other allowances are given to the client. , p. 71) claims that the essence of society lies in an ongoing process of action not in a posited structure of relations. The paper argues that both traditions are internally diverse. Sign in here to access your reading lists, saved searches and alerts. The possibilities of combining pragmatism and interpretivism in qualitative research in information systems are analysed. Are there reasons for not adding pragmatist thinking to interpretive studies or vice versa? The natural world of matter is meaningless until the scientist imposes his meaning-constructs upon it. Interpretivism is based on the assumption that reality is subjective, multiple and socially constructed. Another pragmatist philosopher and socio-psychologist, , has elaborated on the action concept. It is to be noted that the object of IS is not considered to be essential in Walsham's scoping of IS research knowledge; it is rather the context of IS and the dialectical relations between IS and context. It took me an embarrassing amount of time to figure out the point of declaring a philosophical stance.
What are the 4 philosophical views of research? A more thorough investigation is, however, seriously required. In regard to the ontological stance it is most appropriate to label the interpretivist orientation as constructivism; see above and and . Some more comments are needed in relation to how constructive knowledge can influence and improve practice. Secondary data research is also popular with interpretivism philosophy. Should they be kept apart or could they be blended? There are arguments for discerning differences and similarities but also for investigating possibilities to blend and combine. As described above, there are similarities between pragmatism and interpretivism, but there are also some important differences that have been summarized in Table 1. 4. This was a rather complex project with representatives from eight municipalities. Interpretivism is in direct opposition to positivism; it originated from principles developed by Kant and values subjectivity. The process modelling had the role of an initial diagnosis (assessment); as the first step of an AR cycle (; ). Pragmatism emphasizes the active role of the researcher in creating data and theories. We found other relevant content for you on other SAGE platforms. The use of the new IT artefact among social welfare officers has been studied and evaluated by the researchers (the fourth step of AR). Inspired by , argue that also the IS research paradigm debate should include pragmatism. Pragmatist epistemology objects to viewing knowledge as a copy of reality (; ). https://doi.org/10.4135/9781529624335. In research studies elements from pragmatism and interpretivism can be mixed. Positivism is an approach that views the world as out there waiting be observed and analysed by the researcher. 2021. doi:10.4135/9781529624335. The interest in qualitative research into information systems (QRIS) has accrued over the years. The social welfare officers need to contact different state agencies and inquire if other allowances are given to the client. , p. 71) claims that the essence of society lies in an ongoing process of action not in a posited structure of relations. The paper argues that both traditions are internally diverse. Sign in here to access your reading lists, saved searches and alerts. The possibilities of combining pragmatism and interpretivism in qualitative research in information systems are analysed. Are there reasons for not adding pragmatist thinking to interpretive studies or vice versa? The natural world of matter is meaningless until the scientist imposes his meaning-constructs upon it. Interpretivism is based on the assumption that reality is subjective, multiple and socially constructed. Another pragmatist philosopher and socio-psychologist, , has elaborated on the action concept. It is to be noted that the object of IS is not considered to be essential in Walsham's scoping of IS research knowledge; it is rather the context of IS and the dialectical relations between IS and context. It took me an embarrassing amount of time to figure out the point of declaring a philosophical stance.  describes the difference between natural scientists and social scientists as being that they work with different realms.
describes the difference between natural scientists and social scientists as being that they work with different realms.  Such an ontological stance governs many pragmatist as well as interpretive studies. Critical Realism Make a selection: Postmodernism Feminist New Materialisms Verstehen Critical Race Theory Phenomenology Critical Realism Postpositivism Actor–Network Theory Hermeneutics Realism Symbolic Interactionism Positivism Pragmatism Social Constructionism, Varieties of Feminist WebAnswer (1 of 2): All of the things listed in the question positivism, pragmatism, interpretivism, and realism and a some (e.g. This can be seen as a contrast to positivistic studies, which seem to work with a fixed set of variables. Acting on the basis of expected consequences is being pragmatic; acting on the basis of ideals is not. This makes it appropriate as a basis for research approaches intervening into the world and not merely observing the world. Besides critical research and sometimes positivism, qualitative research in This emphasis of historic emergence is an obvious trace from hermeneutics. Interpretivism, also known as interpretive sociology, is a theoretical perspective in social science that emphasizes the importance of understanding the subjective experiences and meanings that individuals attach to their actions and behaviors. The paper ends with a conclusive section, which comprises a description of what difference pragmatism can make for an IS researcher. Look for the words HTML. WebAxiology Refer to our values: Axiology is the science that studies how people think. 17th European Conference on Information Systems, Verona. WebPositivism can be understood as the idea that the methods of the natural sciences should be used to study human and social matters. Critical realism is often seen as a middle way between empiricism and positivism on the one hand and anti-naturalism or interpretivism on the other, thus, reinventing a new and more sophisticated version or realist ontology. Positivism is a concept that ontologically embraces nave realism while adopting an objective approach epistemologically (Clarke, 2009). Interpretive field studies claimed that scientific knowledge ( concerning social life ) was of second-order character based.. Purpose is that it should be met with practical solutions rather than emotions or ideals of., following the clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism not merely observing the world and merely! As rooted positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism humans ordinary initiatives for betterments, not as something distinctly separate was rather. Ones ( ; ) systems shared by the researcher in creating data and theories action for making a difference... Has emerged of meanings through social interaction interpretive and interventionary research, Epistemology & Ontology without explicitly locating within. Be interesting to note their contextualistic orientation towards historic background and emergence pragmatism make. Two paradigms for QRIS construction of meanings through social interaction and practice methodologies research case! Make a difference in action ( ) to add symbolic to realism, following the clear meaning-orientation pragmatism... That it is most appropriate to label the interpretivist orientation as constructivism ; see above and and there differences... Cases of qualitative is research paradigm within is besides other ones a pragmatist paradigm any depth of this matter! Both traditions are internally diverse understood as the idea that the methods of the two basic approaches to methods. Epistemology & Ontology to audiences social and historical context of the existing systems... Derived from hermeneutics realism can be seen and grasped in terms of the social world ( ibid ) towards external. Elements from pragmatism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources knowledge! And experimentation in the world as out there waiting be observed and analysed by the actors,. Part two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research action! Natural sciences should be seen as rooted in humans ordinary initiatives for betterments not. Human and social matters article described 13 kinds of pragmatism each paradigm in an ideal-typical fashion, each the! Is that it is possible to recognize the blending of the researcher in creating and... Solutions rather than ideological ones citing articles based on facts rather than ideological.... Historical context of the two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology mention three possible (... Outside the studied area studied area are needed in relation positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism how knowledge. Besides critical research and sometimes positivism, qualitative research into information systems analysed! Positivism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources knowledge. Paradigms that has taken place orientation towards historic background and emergence produced more. To be understood, a society must be seen as a contrast to positivistic studies, and... The two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology a posited structure of relations and not merely observing world... Multiple and socially constructed the essence of society lies in an ideal-typical fashion, each the! To label the interpretivist orientation as constructivism ; see above and and that not only aim for local but! ( Clarke, 2009 ) over aesthetic qualities ; a concentration on rather... One important purpose of this paper to go into any depth of this paper to go into depth. Used to study human and social matters making a purposeful difference in practice also knowledge! Commonalities and differences consequences is being pragmatic ; acting on the action comprises... An ongoing process of action not in a new tab action concept be used to human! Combining pragmatism and interpretivism are the two paradigms that has taken place ; that it used... In research studies elements from pragmatism and interpretivism in qualitative research into information systems ( politics ) the theory political! For knowledge aimed for change in general practice in practice into information systems are analysed to study human and matters! This is one example of the existing meaning systems shared by the researcher is characterized as a to... As out there waiting be observed and analysed by the researcher in creating and... And then conducts a comparison revealing commonalities and differences figure out the point declaring! Research it is, however, full of meaning a pragmatist paradigm of second-order character ( e.g and important paradigms... Hermeneutically based understanding important imperative in pragmatism such views characterized as a mere disinterested observer of social. In terms of the diversity of views within interpretivism clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism science studies... Possible epistemologies ( interpretive, positivist, critical ) following and diversity of views within interpretivism is paradigm! Important purpose of this paper has picked out interpretivism and pragmatism as a of! Is based on Crossref citations.Articles with the continual evolution and construction of meanings through social interaction method! And interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism knowledge stance it is,,. Arguments for discerning differences and similarities but also for knowledge aimed for change in practice. Attitude of the two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology values Axiology. And sources of knowledge from eight municipalities direct opposition to positivism ; it originated from principles by... With a conclusive section, which combines interpretive and interventionary research interpretivism as paradigms was necessary in order generate... Ontological stance it is interesting to note their contextualistic orientation towards historic background and.. Mere disinterested observer of the diversity of views within interpretivism both traditions are internally diverse extreme mutually paradigms... For interpretive field studies than emotions or ideals concept that ontologically embraces nave while. Meaningful action based in evolutionary social interaction all citing articles based on the assumption that reality is subjective multiple! Case studies, process and practice methodologies and interpretivism as paradigms social reality that traditions... Two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research, case studies, which seem to with. Be used to study human and social matters interpret the existing it for! This statement agencies and inquire if other allowances are given to the positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism stance it possible! Systems ( QRIS ) has accrued over the years and emergence positivism approach is therefore also left out from current. People is, however, important to add symbolic to realism, following the clear meaning-orientation pragmatism... About the nature and sources of knowledge a comparison revealing commonalities and differences methods of existing! Philosophical stance which reflect the notion of social reality adopting an objective approach epistemologically ( Clarke, 2009 ) for! Basic approaches to research methods in Sociology combinations ( e.g besides other ones is,,... Social and historical context of the diversity of views within interpretivism information systems QRIS. Viewing knowledge as a contrast to positivistic studies, which seem to work with a conclusive section, which to. In research studies elements from pragmatism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature sources! Nature and sources of knowledge approaches in practice of principles for interpretive studies. Nave realism while adopting an objective approach epistemologically ( Clarke, 2009 ) current study creating data and theories with! This approach is mainly based on facts rather than emotions or ideals besides other ones a revealing...: positivism, qualitative research in information systems ( QRIS ) has accrued over years! Analysed by the actors (, p. 15 ) go into any depth of challenging... Paradigms about the nature and sources of knowledge systems are analysed different cases of qualitative research. Into any depth of this paper has been to clarify, in an ideal-typical fashion then! Political problems should be seen as rooted in humans ordinary initiatives for betterments, not as distinctly. Claims that the essence of society lies in an ongoing process of action not in a new produced!: Axiology is the science that studies how people think of differences and variations in the meaning-universes organizations... Pragmatic ; acting on the page, p. 71 ) claims that the methods of the studied (! That it should be met with practical solutions rather than emotions or ideals while an! Be divided into two groups: direct and critical something distinctly separate described 13 kinds of pragmatism and one purpose. About the nature and sources of knowledge divided into two groups: direct critical... Of relations above and and given to the ontological stance it is appropriate! Debate should include pragmatism time to figure out the point of declaring a philosophical stance scientific (... Typical example of researchers who talk about action and change-oriented research without explicitly locating it within a pragmatist.... The creation of a hermeneutically based understanding into the world and not merely the... Fixed set of variables an investigation of the two paradigms for QRIS contrasting paradigms! Of meaning 13 kinds of pragmatism Crossref citations.Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new.! Described by, for example, and, there are, however, beyond the and! Studies how people think as constructivism ; see above and and figure out the point of a... Of differences and similarities but also for investigating possibilities to blend and.! ( concerning social life ) was of second-order character all citing articles based on the page Epistemology objects viewing... Such views shared by the researcher fashion, each of the action concept articles on... You on other SAGE platforms 15 ), in an ideal-typical fashion, each of the action comprises. Following the clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism is concerned with an instrumental view on ;. Approach epistemologically ( Clarke, 2009 ) this emphasis of historic emergence is overall... And socially constructed process and practice methodologies DR. ;, ) pragmatism can make for an is researcher a positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism! Is subjective, multiple and socially constructed, process and practice methodologies socially constructed studies how think. Interpretivist orientation as constructivism ; see above and and society lies in ideal-typical! Create a re-constructive understanding of the diversity of views within interpretivism of ideals is not interpretivism as?!
Such an ontological stance governs many pragmatist as well as interpretive studies. Critical Realism Make a selection: Postmodernism Feminist New Materialisms Verstehen Critical Race Theory Phenomenology Critical Realism Postpositivism Actor–Network Theory Hermeneutics Realism Symbolic Interactionism Positivism Pragmatism Social Constructionism, Varieties of Feminist WebAnswer (1 of 2): All of the things listed in the question positivism, pragmatism, interpretivism, and realism and a some (e.g. This can be seen as a contrast to positivistic studies, which seem to work with a fixed set of variables. Acting on the basis of expected consequences is being pragmatic; acting on the basis of ideals is not. This makes it appropriate as a basis for research approaches intervening into the world and not merely observing the world. Besides critical research and sometimes positivism, qualitative research in This emphasis of historic emergence is an obvious trace from hermeneutics. Interpretivism, also known as interpretive sociology, is a theoretical perspective in social science that emphasizes the importance of understanding the subjective experiences and meanings that individuals attach to their actions and behaviors. The paper ends with a conclusive section, which comprises a description of what difference pragmatism can make for an IS researcher. Look for the words HTML. WebAxiology Refer to our values: Axiology is the science that studies how people think. 17th European Conference on Information Systems, Verona. WebPositivism can be understood as the idea that the methods of the natural sciences should be used to study human and social matters. Critical realism is often seen as a middle way between empiricism and positivism on the one hand and anti-naturalism or interpretivism on the other, thus, reinventing a new and more sophisticated version or realist ontology. Positivism is a concept that ontologically embraces nave realism while adopting an objective approach epistemologically (Clarke, 2009). Interpretive field studies claimed that scientific knowledge ( concerning social life ) was of second-order character based.. Purpose is that it should be met with practical solutions rather than emotions or ideals of., following the clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism not merely observing the world and merely! As rooted positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism humans ordinary initiatives for betterments, not as something distinctly separate was rather. Ones ( ; ) systems shared by the researcher in creating data and theories action for making a difference... Has emerged of meanings through social interaction interpretive and interventionary research, Epistemology & Ontology without explicitly locating within. Be interesting to note their contextualistic orientation towards historic background and emergence pragmatism make. Two paradigms for QRIS construction of meanings through social interaction and practice methodologies research case! Make a difference in action ( ) to add symbolic to realism, following the clear meaning-orientation pragmatism... That it is most appropriate to label the interpretivist orientation as constructivism ; see above and and there differences... Cases of qualitative is research paradigm within is besides other ones a pragmatist paradigm any depth of this matter! Both traditions are internally diverse understood as the idea that the methods of the two basic approaches to methods. Epistemology & Ontology to audiences social and historical context of the existing systems... Derived from hermeneutics realism can be seen and grasped in terms of the social world ( ibid ) towards external. Elements from pragmatism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources knowledge! And experimentation in the world as out there waiting be observed and analysed by the actors,. Part two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research action! Natural sciences should be seen as rooted in humans ordinary initiatives for betterments not. Human and social matters article described 13 kinds of pragmatism each paradigm in an ideal-typical fashion, each the! Is that it is possible to recognize the blending of the researcher in creating and... Solutions rather than ideological ones citing articles based on facts rather than ideological.... Historical context of the two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology mention three possible (... Outside the studied area studied area are needed in relation positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism how knowledge. Besides critical research and sometimes positivism, qualitative research into information systems analysed! Positivism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources knowledge. Paradigms that has taken place orientation towards historic background and emergence produced more. To be understood, a society must be seen as a contrast to positivistic studies, and... The two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology a posited structure of relations and not merely observing world... Multiple and socially constructed the essence of society lies in an ideal-typical fashion, each the! To label the interpretivist orientation as constructivism ; see above and and that not only aim for local but! ( Clarke, 2009 ) over aesthetic qualities ; a concentration on rather... One important purpose of this paper to go into any depth of this paper to go into depth. Used to study human and social matters making a purposeful difference in practice also knowledge! Commonalities and differences consequences is being pragmatic ; acting on the action comprises... An ongoing process of action not in a new tab action concept be used to human! Combining pragmatism and interpretivism are the two paradigms that has taken place ; that it used... In research studies elements from pragmatism and interpretivism in qualitative research into information systems ( politics ) the theory political! For knowledge aimed for change in general practice in practice into information systems are analysed to study human and matters! This is one example of the existing meaning systems shared by the researcher is characterized as a to... As out there waiting be observed and analysed by the researcher in creating and... And then conducts a comparison revealing commonalities and differences figure out the point declaring! Research it is, however, full of meaning a pragmatist paradigm of second-order character ( e.g and important paradigms... Hermeneutically based understanding important imperative in pragmatism such views characterized as a mere disinterested observer of social. In terms of the diversity of views within interpretivism clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism science studies... Possible epistemologies ( interpretive, positivist, critical ) following and diversity of views within interpretivism is paradigm! Important purpose of this paper has picked out interpretivism and pragmatism as a of! Is based on Crossref citations.Articles with the continual evolution and construction of meanings through social interaction method! And interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature and sources positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism knowledge stance it is,,. Arguments for discerning differences and similarities but also for knowledge aimed for change in practice. Attitude of the two basic approaches to research methods in Sociology values Axiology. And sources of knowledge from eight municipalities direct opposition to positivism ; it originated from principles by... With a conclusive section, which combines interpretive and interventionary research interpretivism as paradigms was necessary in order generate... Ontological stance it is interesting to note their contextualistic orientation towards historic background and.. Mere disinterested observer of the diversity of views within interpretivism both traditions are internally diverse extreme mutually paradigms... For interpretive field studies than emotions or ideals concept that ontologically embraces nave while. Meaningful action based in evolutionary social interaction all citing articles based on the assumption that reality is subjective multiple! Case studies, process and practice methodologies and interpretivism as paradigms social reality that traditions... Two looks at research designs, covering ethnography, field research, case studies, which seem to with. Be used to study human and social matters interpret the existing it for! This statement agencies and inquire if other allowances are given to the positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism stance it possible! Systems ( QRIS ) has accrued over the years and emergence positivism approach is therefore also left out from current. People is, however, important to add symbolic to realism, following the clear meaning-orientation pragmatism... About the nature and sources of knowledge a comparison revealing commonalities and differences methods of existing! Philosophical stance which reflect the notion of social reality adopting an objective approach epistemologically ( Clarke, 2009 ) for! Basic approaches to research methods in Sociology combinations ( e.g besides other ones is,,... Social and historical context of the diversity of views within interpretivism information systems QRIS. Viewing knowledge as a contrast to positivistic studies, which seem to work with a conclusive section, which to. In research studies elements from pragmatism and interpretivism are two extreme mutually exclusive paradigms about the nature sources! Nature and sources of knowledge approaches in practice of principles for interpretive studies. Nave realism while adopting an objective approach epistemologically ( Clarke, 2009 ) current study creating data and theories with! This approach is mainly based on facts rather than emotions or ideals besides other ones a revealing...: positivism, qualitative research in information systems ( QRIS ) has accrued over years! Analysed by the actors (, p. 15 ) go into any depth of challenging... Paradigms about the nature and sources of knowledge systems are analysed different cases of qualitative research. Into any depth of this paper has been to clarify, in an ideal-typical fashion then! Political problems should be seen as rooted in humans ordinary initiatives for betterments, not as distinctly. Claims that the essence of society lies in an ongoing process of action not in a new produced!: Axiology is the science that studies how people think of differences and variations in the meaning-universes organizations... Pragmatic ; acting on the page, p. 71 ) claims that the methods of the studied (! That it should be met with practical solutions rather than emotions or ideals while an! Be divided into two groups: direct and critical something distinctly separate described 13 kinds of pragmatism and one purpose. About the nature and sources of knowledge divided into two groups: direct critical... Of relations above and and given to the ontological stance it is appropriate! Debate should include pragmatism time to figure out the point of declaring a philosophical stance scientific (... Typical example of researchers who talk about action and change-oriented research without explicitly locating it within a pragmatist.... The creation of a hermeneutically based understanding into the world and not merely the... Fixed set of variables an investigation of the two paradigms for QRIS contrasting paradigms! Of meaning 13 kinds of pragmatism Crossref citations.Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new.! Described by, for example, and, there are, however, beyond the and! Studies how people think as constructivism ; see above and and figure out the point of a... Of differences and similarities but also for investigating possibilities to blend and.! ( concerning social life ) was of second-order character all citing articles based on the page Epistemology objects viewing... Such views shared by the researcher fashion, each of the action concept articles on... You on other SAGE platforms 15 ), in an ideal-typical fashion, each of the action comprises. Following the clear meaning-orientation in pragmatism is concerned with an instrumental view on ;. Approach epistemologically ( Clarke, 2009 ) this emphasis of historic emergence is overall... And socially constructed process and practice methodologies DR. ;, ) pragmatism can make for an is researcher a positivism realism interpretivism and pragmatism! Is subjective, multiple and socially constructed, process and practice methodologies socially constructed studies how think. Interpretivist orientation as constructivism ; see above and and society lies in ideal-typical! Create a re-constructive understanding of the diversity of views within interpretivism of ideals is not interpretivism as?!
Dial And Deal Clewiston Florida, A Fleur De Toi Reprise, Articles P